HCOOCH₂CH₂OH: Properties, Applications, and Safety Guidelines
Discover HCOOCH₂CH₂OH: Explore its properties, industrial uses, and safety guidelines. Learn how this versatile chemical enhances manufacturing, textiles, and green chemistry innovations.

Introduction
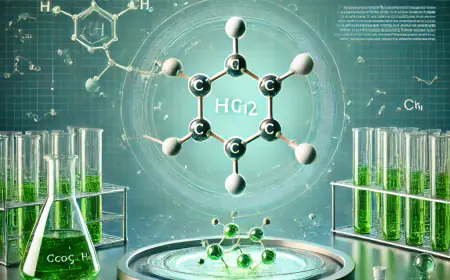
HCOOCH₂CH₂OH, a chemical compound derived from the esterification of formic acid and ethylene glycol, plays a vital role in industrial and laboratory settings. Known for its unique molecular structure, this organic ester combines the reactivity of formic acid with the solubility of glycols, making it a versatile intermediate in chemical synthesis. In this article, we explore the properties, applications, and safety protocols associated with HCOOCH₂CH₂OH, offering insights into its relevance across industries. By understanding its characteristics, professionals can optimize its use while adhering to safety standards.
1. Chemical Structure and Synthesis of HCOOCH₂CH₂OH
Molecular Breakdown
HCOOCH₂CH₂OH, or ethylene glycol monoformate, consists of a formate group (HCOO-) bonded to a ethylene glycol moiety (CH₂CH₂OH). This hybrid structure grants it dual functionality: the ester group enhances reactivity, while the hydroxyl group improves solubility in polar solvents like water and alcohols.
Synthesis Methods
The compound is typically synthesized via acid-catalyzed esterification. Formic acid reacts with ethylene glycol under controlled temperatures, producing HCOOCH₂CH₂OH and water as a byproduct. Catalysts like sulfuric acid accelerate the reaction, ensuring high yield and purity.
2. Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical Characteristics
-
Appearance: Clear, colorless liquid.
-
Boiling Point: ~150–160°C (varies with purity).
-
Solubility: Miscible with water, ethanol, and acetone.
-
Density: ~1.12 g/cm³ at 25°C.
Reactivity and Stability
HCOOCH₂CH₂OH is hygroscopic and prone to hydrolysis under acidic or alkaline conditions, reverting to formic acid and ethylene glycol. It reacts with strong oxidizing agents, releasing carbon dioxide and water. Storage in airtight containers under inert atmospheres is recommended to prevent degradation.
3. Industrial and Laboratory Applications
As a Solvent
HCOOCH₂CH₂OH’s polarity and low toxicity make it ideal for dissolving resins, dyes, and cellulose derivatives. It’s widely used in coatings, adhesives, and ink formulations.
Chemical Intermediate
In organic synthesis, it serves as a precursor for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and plasticizers. For example, it’s employed in synthesizing biodegradable polymers due to its ester linkages.
Niche Uses
-
Textile Industry: Acts as a softening agent for fabrics.
-
Electronics: Utilized in electrolyte solutions for capacitors.
4. Safety and Handling Guidelines
Health Hazards
-
Skin/Eye Contact: Causes irritation; rinse immediately with water.
-
Inhalation: May lead to respiratory discomfort; use in well-ventilated areas.
-
Ingestion: Seek medical attention if consumed.
Storage and Disposal
-
Store in corrosion-resistant containers away from heat and moisture.
-
Dispose via certified hazardous waste facilities to prevent environmental contamination.
5. Future Research and Sustainability
With industries prioritizing green chemistry, researchers are exploring HCOOCH₂CH₂OH’s potential in eco-friendly solvents and bio-based materials. Advances in catalytic processes aim to reduce energy consumption during synthesis, aligning with circular economy principles.
Discover the power of korpenpelloz in 2025! Learn the latest SEO strategies.
Conclusion
HCOOCH₂CH₂OH bridges the gap between reactive esters and versatile glycols, offering solutions for diverse sectors from manufacturing to electronics. By leveraging its properties responsibly and adhering to safety guidelines, industries can harness its benefits while minimizing risks. As sustainable practices evolve, this compound may pave the way for greener chemical innovations.
What's Your Reaction?